
1.2.1. Assessment of the resolution of surface albedo satellite data for monitoring the Sahara desert#
Production date: 30-09-2024
Produced by: Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR )
🌍 Use case: Estimating desertification using surface albedo data#
❓ Quality assessment question#
• Can satellite albedo datasets be used to estimate the expansion of the Sahara desert?
The Sahara, Earth’s largest hot desert, has expanded in recent decades. Existing studies indicates a sustained enlargement of the dry zone on both annual and seasonal timescales [1]. This implies risks to ecosystems, pastoral livelihoods, food and water security, and infrastructure across North and West Africa. Multiple regional studies document intensified desertification pressures in precisely the areas our analysis targets: sand‐dune encroachment around Nouakchott in Mauritania [2]; degradation and desertification sensitivity along the Algerian steppe, Sahara margin, where large‐scale countermeasures such as the “Green Dam” have been evaluated [3]; dune reactivation and wind‐erosion impacts in Niger [4]; active dune migration in the Libyan Ubārī Sand Sea [5]; and increased mobile dunes around Lake Chad and northern Chad since the 1970s [6]. In this assessment, we test whether satellite‐derived surface albedo from the Copernicus CDS (10-daily, 1-km; SPOT-VGT/PROBA-V, v2) can monitor desert expansion signals by mapping spatial albedo patterns and their changes comparing the data for two year, the winter season 2006-2007 and 2019-2020 (November to February, NDJF). Evaluating desertification during the NDJF[FM1.1] (November-January-February) period is crucial because this is often the dry season in many regions, making it the most vulnerable time for desertification to worsen. Albedo is a suitable proxy for surface state in arid lands because brightening often accompanies exposure or stabilization of bare sands and crusts, while darkening may reflect seasonal greening or increased surface moisture. Using seasonally consistent composites and quality screening, we quantify “desert-like” area via albedo masks and compute area changes on the native grid. The results reveal a small net increase in very bright desert‐like area across the Sahara, with the largest gains concentrated in the western–central Sahara (notably Mali and Mauritania), [FM2.1]aligning with the independent evidence cited above [1–6]. This supports the use of CDS surface albedo data as a powerful tool for monitoring desertification dynamics and regional hotspots of change.
📢 Quality assessment statement#
These are the key outcomes of this assessment
The seasonal albedo maps provide a clear, side-by-side view of surface reflectance in two benchmark years, making spatial changes in bright, desert-like areas easy to spot.
📋 Methodology#
The methodology adopted for the analysis is split into the following steps:
1. Choose the data to use and set up the code
Import all the relevant packages.
2. Data loading and preparation
Load monthly albedo data
Dataset inspection and Sahara albedo extraction
QFLAG filtering + Plot helpers 3. Plot and describe the results.
Sahara study area maps with country names
Detecting and Visualizing Sahara Desert Expansion from Albedo (NDJF, 2006→2019)
Quantifying Desertification by Country within the Sahara Study Domain
Validate “new-desert” pixels and inspect their values
Pixel count analysis of albedo map plots – Summer 2006 vs 2019
Plot albedo change map (2019 − 2006)
📈 Analysis and results#
1. Choose the data to use and set up the code#
Import all the relevant packages#
In this section, we import all the relevant packages required to run the notebook.
2. Data loading and preparation#
Load monthly albedo data#
satellite='spot'
100%|██████████| 8/8 [00:00<00:00, 9.86it/s]
/data/common/miniforge3/envs/wp5/lib/python3.12/site-packages/earthkit/data/readers/netcdf/fieldlist.py:202: FutureWarning: In a future version of xarray the default value for data_vars will change from data_vars='all' to data_vars=None. This is likely to lead to different results when multiple datasets have matching variables with overlapping values. To opt in to new defaults and get rid of these warnings now use `set_options(use_new_combine_kwarg_defaults=True) or set data_vars explicitly.
return xr.open_mfdataset(
satellite='proba'
100%|██████████| 7/7 [00:00<00:00, 41.57it/s]
/data/common/miniforge3/envs/wp5/lib/python3.12/site-packages/earthkit/data/readers/netcdf/fieldlist.py:202: FutureWarning: In a future version of xarray the default value for data_vars will change from data_vars='all' to data_vars=None. This is likely to lead to different results when multiple datasets have matching variables with overlapping values. To opt in to new defaults and get rid of these warnings now use `set_options(use_new_combine_kwarg_defaults=True) or set data_vars explicitly.
return xr.open_mfdataset(
Dataset inspection and Sahara albedo extraction#
=== SPOT ===
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 20GB
Dimensions: (time: 96, latitude: 1456, longitude: 3920)
Coordinates:
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 768B 2006-01-10 ... 2013-12-10
* latitude (latitude) float64 12kB 28.0 27.99 27.98 ... 15.03 15.02 15.01
* longitude (longitude) float64 31kB -10.0 -9.991 -9.982 ... 24.98 24.99
Data variables:
crs (time) |S1 96B b'' b'' b'' b'' b'' b'' ... b'' b'' b'' b'' b''
AL_BH_BB (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_BB_ERR (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_NI (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_NI_ERR (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_VI (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_VI_ERR (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AGE (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
NMOD (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
QFLAG (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
Attributes: (12/23)
time_coverage_end: 2006-01-10T23:59:59Z
time_coverage_start: 2005-12-21T00:00:00Z
platform: SPOT-5
sensor: VEGETATION-2
Conventions: CF-1.6
archive_facility: VITO
... ...
source: Derived from EO satellite imagery
title: 10 daily broadband hemispherical surface albedo der...
creator_name: Iskander Benhadj
creator_email: iskander.benhadj@vito.be
project: C3S_312b_Lot5
date_created: 2021-03-24
=== PROBA ===
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 16GB
Dimensions: (time: 78, latitude: 1456, longitude: 3920)
Coordinates:
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 624B 2014-01-10 ... 2020-06-10
* latitude (latitude) float64 12kB 28.0 27.99 27.98 ... 15.03 15.02 15.01
* longitude (longitude) float64 31kB -10.0 -9.991 -9.982 ... 24.98 24.99
Data variables:
crs (time) |S1 78B b'' b'' b'' b'' b'' b'' ... b'' b'' b'' b'' b''
AL_BH_BB (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_BB_ERR (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_NI (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_NI_ERR (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_VI (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AL_BH_VI_ERR (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
AGE (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
NMOD (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
QFLAG (time, latitude, longitude) float32 2GB dask.array<chunksize=(1, 1456, 3920), meta=np.ndarray>
Attributes: (12/23)
time_coverage_end: 2014-01-10T23:59:59Z
time_coverage_start: 2013-12-21T00:00:00Z
platform: PROBA-V
sensor: VEGETATION
Conventions: CF-1.6
archive_facility: VITO
... ...
source: Derived from EO satellite imagery
title: 10 daily broadband hemispherical surface albedo der...
creator_name: Iskander Benhadj
creator_email: iskander.benhadj@vito.be
project: C3S_312b_Lot5
date_created: 2021-03-31
QFLAG filtering + Plot helpers#
3. Plot and describe the results.#
Sahara study area maps with country names#
Figure 1. Study domain for the Sahara analysis. Left: West Africa context with the red rectangle showing the bounding box used for data extraction (28°N–15°N, 10°W–25°E; Plate Carrée). Right: Zoomed view of the box with national borders and labels (Morocco, Western Sahara, Mauritania, Mali, Algeria, Niger, Libya, Chad, Sudan, Egypt, and Burkina Faso) to indicate where changes are assessed.
Detecting and Visualizing Sahara Desert Expansion from Albedo (NDJF, 2006→2019)#
We build NDJF (Nov–Feb) albedo composites for two epochs—2006 from SPOT and 2019 from PROBA—using the same QC mask (Bits 4 & 7) via seasonal_mean_bits47. If 2019 NDJF is incomplete, we fall back to the latest available PROBA year. We then restrict all comparisons to the common valid footprint (valid_both). Pixel-wise change is computed as Δ = PROBA − SPOT. A pixel is flagged as “new desert” when (i) it was not desert in 2006, (ii) it is desert in 2019, and (iii) it brightened by at least min_delta = 0.02. “Desert” here means broadband hemispherical albedo > thr = 0.35. For context, we also mark pixels that brightened by >0.02 but remained below the threshold. Finally, the figure shows: (top left/right) the two NDJF albedo maps on a shared color scale with the threshold contour; and (bottom) a change map where red pixels are “new desert” (crossed the threshold), and pale yellow pixels brightened but stayed sub-threshold. Grid labels are placed on the left of the SPOT map and the right of the PROBA map for readability, and a single colorbar applies to both top panels.
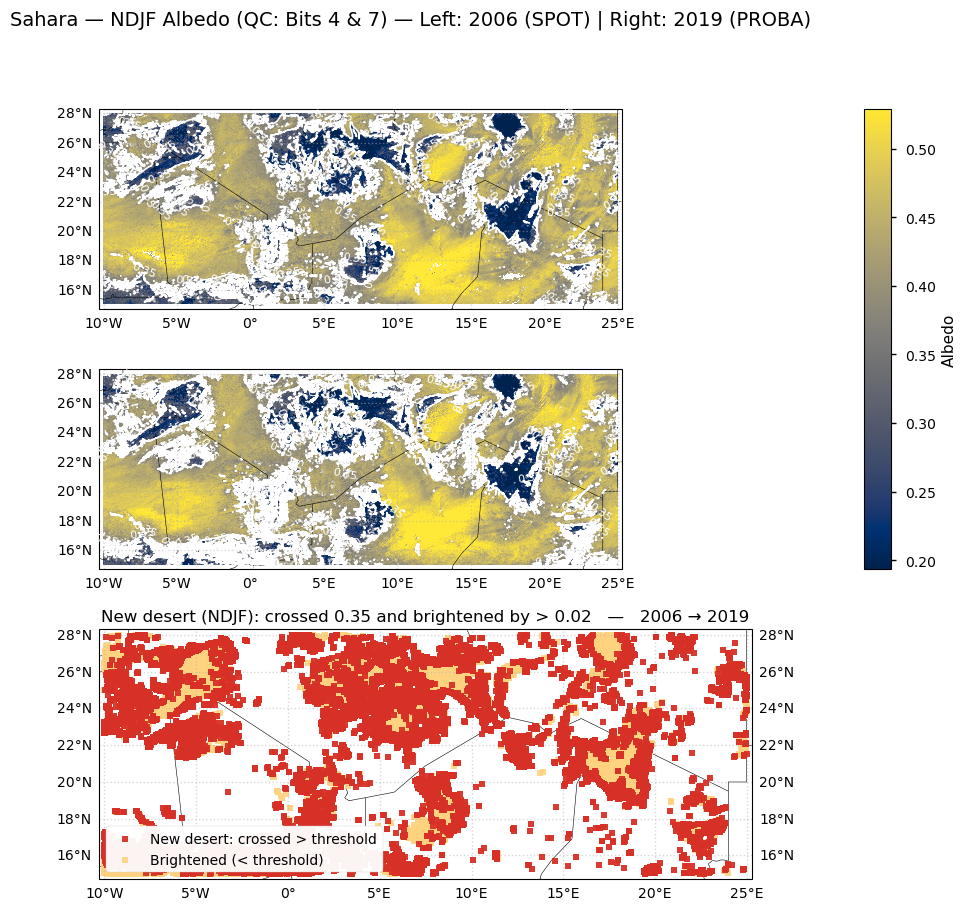
Figure 2. NDJF (Nov–Feb) broadband albedo over the Sahara in 2006 (SPOT, left) and 2019 (PROBA-V, right) after quality control (QFLAG bits 4 & 7: valid inputs and algorithm success). The lower panel highlights change between the two epochs: red pixels brightened by >0.02 and crossed above the 0.35 threshold (“new desert”), while yellow pixels brightened by >0.02 but remained below the threshold. Only the footprint valid in both years is considered.
Quantifying desertification by country within the Sahara study domain#
To quantify desertification in each country inside the Sahara study domain, we (i) mapped pixels that became newly “desert-like” between 2006 and 2019 (crossing an albedo threshold in 2019 but not in 2006) after quality control, (ii) summed those pixels to km² using an equal-area projection, and (iii) normalized by each country’s own area within the study box to report an interpretable percentage of its in-box territory affected. To avoid distorted ratios from tiny border slivers, we filtered out countries with <10,000 km² inside the box. The resulting km² and % values reflect intensity of change within each country across the analyzed portion of the desert.
FULL TABLE — includes countries with tiny slices inside the box (may inflate %):
country new_bright_km2 area_km2_in_bbox pct_of_country_in_bbox area_km2_country_total pct_of_whole_country
Burkina Faso 181 424 42.65 272627 0.07
Mali 37448 880150 4.25 1254111 2.99
Mauritania 20062 500134 4.01 1035382 1.94
Morocco 323 13461 2.40 581713 0.06
Western Sahara 364 15575 2.34 90593 0.40
Algeria 18596 1198624 1.55 2319300 0.80
Egypt 13 1324 0.98 1001772 0.00
Niger 7164 887120 0.81 1181186 0.61
Chad 3826 664675 0.58 1266547 0.30
Libya 3986 978683 0.41 1623739 0.25
Sudan 99 69086 0.14 1856671 0.01
STABLE REPORT — filtered to countries with ≥ 10,000 km² inside the study box:
country new_bright_km2 area_km2_in_bbox pct_of_country_in_bbox area_km2_country_total pct_of_whole_country
Mali 37448 880150 4.25 1254111 2.99
Mauritania 20062 500134 4.01 1035382 1.94
Morocco 323 13461 2.40 581713 0.06
Western Sahara 364 15575 2.34 90593 0.40
Algeria 18596 1198624 1.55 2319300 0.80
Niger 7164 887120 0.81 1181186 0.61
Chad 3826 664675 0.58 1266547 0.30
Libya 3986 978683 0.41 1623739 0.25
Sudan 99 69086 0.14 1856671 0.01
Summary (stable percentages):
- Mali: 4.25% of its study-area footprint (37,448 km² of 880,150 km²)
- Mauritania: 4.01% of its study-area footprint (20,062 km² of 500,134 km²)
- Morocco: 2.40% of its study-area footprint (323 km² of 13,461 km²)
Note: percentages are relative to EACH COUNTRY’S AREA within the study box; tiny-slice countries were excluded to avoid misleading high ratios.
Validate “new-desert” pixels and inspect their values#
This cell turns the NDJF albedo maps for 2006 and 2019 into one table, keeps only pixels that are valid in both years, and then selects the ones that became desert by our rule (2019 albedo > thr, 2006 albedo ≤ thr, and increase ≥ min_delta). It then (a) counts how many pixels meet all three conditions, (b) summarizes their values with min/median/max and percentiles for 2006 albedo, 2019 albedo, and the change (Δ), and (c) prints a small random sample showing latitude, longitude, 2006 albedo, 2019 albedo, and Δ for quick spot-checks.
| latitude | longitude | albedo_2006 | albedo_2019 | delta | check_2019_gt_thr | check_2006_le_thr | check_delta_gt_min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 209 | 28.0 | -8.13 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.02 | True | True | True |
| 210 | 28.0 | -8.12 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.02 | True | True | True |
| 211 | 28.0 | -8.12 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.02 | True | True | True |
| 1154 | 28.0 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.04 | True | True | True |
| 1155 | 28.0 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.04 | True | True | True |
| 1159 | 28.0 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.03 | True | True | True |
| 1160 | 28.0 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.04 | True | True | True |
| 1161 | 28.0 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.05 | True | True | True |
| 1162 | 28.0 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.04 | True | True | True |
| 1163 | 28.0 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.04 | True | True | True |
New-desert rows: 55,644 | Fully consistent with rules: 55,644
Albedo (2006) — min/median/max: 0.03830000013113022 0.335099995136261 0.3499999940395355
Albedo (2019) — min/median/max: 0.3500000238418579 0.3654000163078308 0.5915249586105347
Delta — min/median/max: 0.02000001072883606 0.030000001192092896 0.47872495651245117
p05 2006/2019/delta: 0.308 0.352 0.021
p25 2006/2019/delta: 0.327 0.358 0.024
p50 2006/2019/delta: 0.335 0.365 0.03
p75 2006/2019/delta: 0.343 0.373 0.04
p95 2006/2019/delta: 0.348 0.39 0.061
latitude longitude albedo_2006 albedo_2019 delta
5155039 16.259 -7.866 0.327 0.378 0.051
1259821 25.134 3.402 0.323 0.360 0.038
5557984 15.348 19.857 0.329 0.401 0.072
1910388 23.652 2.036 0.348 0.374 0.025
5037371 16.527 -8.473 0.329 0.368 0.039
5589356 15.277 19.964 0.315 0.352 0.037
5301462 15.929 4.482 0.330 0.383 0.053
5450363 15.589 3.955 0.333 0.357 0.024
1633875 24.286 18.170 0.342 0.420 0.078
5461716 15.562 0.321 0.318 0.358 0.039
Take-home messages#
• Using threshold of surface albedo of 0.35 to separate desert from non-desert areas combined with a increase of surface brightening Δ= surface albedo2019 - surface albedo2006 > 0.02, the year 2019 shows a small expansions of the desert compared to the year 2006, which occurs in different countries in the region and it is larger in Mali and Mauritania. • Pixel-level verification confirms that the flagged locations satisfying the selection rules (surface albedo2019 > 0.35, surface albedo2006 ≤ 0.35, and Δ > 0.02) show values of Δ in the 0.02–0.08 range.
ℹ️ If you want to know more#
References#
[1] Thomas, N., & Nigam, S. (2018). Twentieth-Century Climate Change over Africa: Seasonal Hydroclimate Trends and Sahara Desert Expansion. Journal of Climate, 31(9), 3349–3370.
[2] Gómez, D., Salvador, P., Sanz, J., & Casanova, J. L. (2018). Detecting Areas Vulnerable to Sand Encroachment Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques in Nouakchott (Mauritania). Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1541.
[3] Benhizia, R., Akermi, S., & Bouguerra, H. (2021). Monitoring the Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Green Dam in Djelfa Province, Algeria (1972–2019). Sustainability, 13(14), 7953.
[4] Touré, A. A., Bilal, B., Tidjani, A. D., & Karimoune, S. (2019). Dynamics of wind erosion and impact of vegetation cover and land use in the Sahel: A case study on sandy dunes in southeastern Niger. Catena, 181, 104094.
[5] Els, A., Mayer, P., & Cooksley, G. (2015). Comparison of Two Satellite Imaging Platforms for Evaluating Sand Dune Migration in the Ubari Sand Sea (Libya). The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XL-7/W3, 1375–1382.
[6] Abdoulkader, M. I., Tidjani, A. D., & Aboubakar, I. (2016). Spatial dynamics of mobile dunes, soil crusting and Yobe’s bank retreat in the Niger’s Lake Chad basin (cases of Issari and Bagara). African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 10(6), 151–161.
